

It’s position on primate skulls provides very important information that anthropologists use to understand existing species and fossil species. The foramen magnum is the hole at the base of a skull where the spinal cord exits. Foramen magnum A mountain gorilla walking on four feet Human ancestor species predating the genus homo exhibit only a slight degree of prognathism. Chimpanzees, who share a more recent ancestor with humans 6-10 million years ago, have reduced prognathism. Generally speaking, Gorillas, who share a distant ancestor with humans 12-17 million years ago, have a high degree of facial prognathism. There is a general trend of decreasing facial prognathism along the human evolutionary lineage. Prognathism describes the degree to which an animal’s lower face protrudes forward.
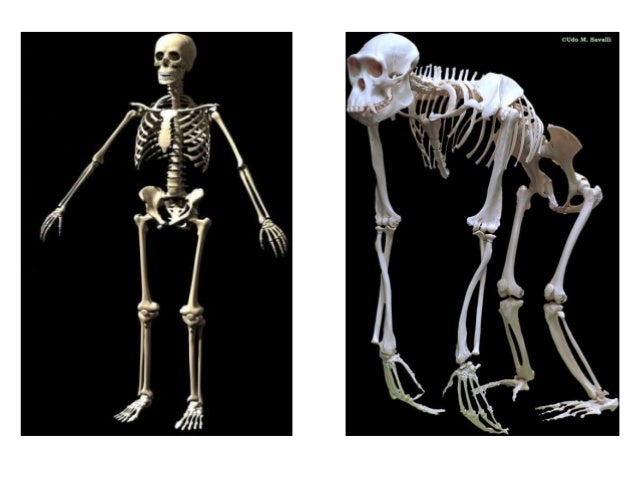
Facial prognathism An eastern lowland gorilla The gorilla skull has therefore evolved to support this diet and a large sagittal crest is the result. Chewing a large volume of leaves requires strong chewing muscles and a skull that can withstand intense strain and bite forces. Gorillas are folivores, meaning they rely mostly on foliage as a food source. The large sagittal crest indicates the attachment of large masticatory muscles (chewing muscles) capable of processing tough foods. In gorillas, however, the sagittal crest is an important muscle attachment site. By running your hand through your hair, you can pretty easily tell humans do not have one. The sagittal crest is a bony ridge on top of some ape skulls that spans the cranium from front to back. What do these features tell us? Sagittal crest A mountain gorilla eating a leaf The canine teeth (in humans, the third tooth over from center of teeth) The hole at the base of the skull where the spinal cord exits The degree to which the lower face protrudes forward From these skull features we can learn about an animal’s diet, mating strategy, posture, and evolutionary history. Each of these features can not only show us how the species differ from each other, but also about how they live. This table describes a few different features present on ape skulls and compares them in humans, chimpanzees, and gorillas. As a result of this size difference, male gorilla skulls are much larger than female gorilla skulls. Male gorillas typically weigh between 300 and 500 pounds, whereas females weigh between 150 to 250 pounds. Gorillas are very sexually dimorphic because male gorillas are much larger than females. This is when there are distinct physical differences between males and females of the same species. Gorilla brains are about 1/3 the size of human brains! A gorilla’s facial bones are much more robust than those of a human, however. The human cranium has a much larger volume than a gorilla’s cranium and houses a much larger brain. Skulls consist of the cranium (the brain case) and the splanchnocranium (the facial bones). Human skulls are 19 cm high, 15 cm long, and 18 cm wide. In fact, the average male gorilla’s skull is 16 cm high, 34 cm long, and 18 cm wide. Gorilla skulls are exceptionally large amongst primates. What is unique about gorilla skull size? A male eastern lowland gorilla Considering the timeline of mammal evolution (with the first mammal arising 65 million years ago), this is quite recent! The close evolutionary histories of gorillas and humans explain many similarities that appear between the species. The lineage that includes chimpanzees and humans diverged from a common ancestor with gorillas about 12-17 million years ago. For more about the difference between apes and gorillas, click here. As such, they are closely related to orangutans, chimpanzees, bonobos, and humans. They are the largest primate on Earth and are also a member of the great apes. There are two species of gorilla and four subspecies: western gorillas (including western lowland gorillas and Cross River gorillas) and eastern gorillas (including eastern lowland gorillas and mountain gorillas). Gorillas are large land mammals that live primarily in Rwanda, the Congo, Uganda, Angola, Cameroon, Central Africa, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and Nigeria depending on the subspecies. What is a gorilla? A western lowland gorilla This article will investigate how our skulls compare and what other interesting information skulls can reveal about a species. In actuality, the skulls of our not-so-distant gorilla relatives are quite similar to ours. They are also incredibly large! Within this colossal animal is a very interesting and complex skull that seems to be very different from a human skull. Gorillas are beautiful and unique creatures.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
